Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a rare pathology and the "lowest form" of osteochondrosis. Due to its anatomical features, this part of the spine is relatively rarely subjected to degeneration. The twelve vertebrae in the class are very tightly connected to each other and are perfectly protected with a kind of muscle bandage, which significantly limits the range of motion between them. The ribs give extra stiffness to the vertebrae.
The most likely cause of chest osteochondrosis is scoliosis, which even develops on the desk. Risk factors for intervertebral disc damage may include:
- hereditary factor;
- malnutrition and overweight;
- work with reduced mobility;
- excessive physical activity;
- age factor and hypothermia;
- instability of vertebral plate segments;
- smoking and nervous exertion;
- contusions, fractures, and injuries of the spine are the most favorable factors in the development of thoracic osteochondrosis.
Symptoms and signs
One of the hallmarks of osteochondrosis of the breast is pain. Divide into standard types:
- Lumbago - dorsago. Manifestation of acute, sudden pain in the affected vertebral discs. The symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are the consequences of a prolonged sitting position when you have to sit at a table for a long time and bend over. Sharp pain (lumbago) occurs when you try to stand up or lift yourself up.
- Dorsalgia. Increased pain when taking deep breaths and moving the torso. The muscles of the back are tense and movement in any region of the spine may be restricted.
Visceral (internal) manifestations
With osteochondrosis of the chest, the symptoms are rich in internal (visceral) manifestations.
Defeat of the upper chest nerve roots causes pain in the esophagus and pain in the pharynx.
Pressure on the affected area of the spine causes increased pain. It can be paroxysmal.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, manifested by pain in the stomach, indicate damage to the nerve endings in the middle chest region, which causes increased pain if you lie on your back for a long time.
Compression of spinal roots 8 and 9 causes pain in the duodenal region. The sensitivity of the front of the abdominal wall is impaired.
Abnormal motility of the stomach (secretion and peristalsis) is a characteristic symptom of chest osteochondrosis.
Result:
- nausea and vomiting;
- heartburn;
- pain in the left hypochondria;
- bloating;
- diarrhea or constipation.
Duodenal (secretory and motor) dysfunctions lead to:
- nausea and belching;
- there is a feeling of pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
Very often, osteochondrosis of the thoracic region presents with symptoms characteristic of other diseases, such as angina pectoris. However, they experience pain in the heart: cutting, pressure, burning of the heart, or squeezing of the throat.
With laryngospasm, as a result of pathology at the level of the cervical vertebrae, symptoms appear:
- shortness of breath and cough;
- panting;
- shortness of breath.
In the treatment of chest osteochondrosis, the symptoms and manifestations of which are similar to those of pulmonary pathology, their involvement in spinal disease should be precisely determined.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Diagnostic data based on X-rays will assist in compiling a treatment plan for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. Such a study provides a clear picture of the treatment of osteochondrosis of the chest, as X-rays indicating proliferation of the vertebral bodies and changes in the distance between the vertebrae (loss of height) are a characteristic symptom of this disease.
Based on the data of the diagnostic test, the leading symptom is determined, the clinical diagnosis is clarified, which allows to determine the correct tactics.
The treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine depends directly on the syndromes, the stage of development and the presence of background diseases.
A conservative method combined with complex, step-by-step treatment is used to relieve pain, restore impaired spinal nerve function, and prevent the progression of degenerative changes in the structure of the spine.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis involves a number of physiotherapy procedures:
- inductometry and electrophoresis;
- laser therapy and vacuum therapy;
- sinusoidal modeled and diadynamic currents;
- magneto and pharmacopuncture;
- acupuncture.
Drug therapy:
- vascular diuretics and muscle relaxants (muscle relaxants and venotonics);
- paravertebral novokoin blockade.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy for thoracic osteochondrosis is a major stage in the healing process. It strengthens the muscles and mobility of the spine. Exercise against chest osteochondrosis improves ventilation in patients whose deep breathing causes pain.
Gymnastics for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is effective:
- when the spine is tense;
- when adjusting for proper breathing.
But we must not forget that chest osteochondrosis exercise is only effective if all the causes of the disease are identified and eliminated.
If the prescribed treatment has not yielded positive results, various surgical interventions will be used based on the symptoms expressed and the degree of death.
Cervico-thoracal osteochondrosis
Cervicothoracal osteochondrosis is a disease caused by processes affecting the plates of the cervical spine (degenerative-dystrophic).
Vertebrae located close to each other are not adequately protected by a relatively poorly developed musculoskeletal system. Even the slightest tension in the neck causes myelopathy.
Main symptoms
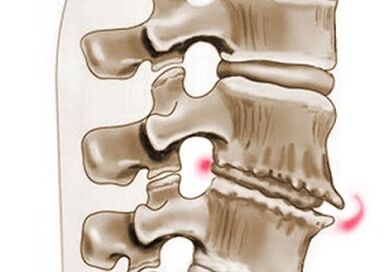
Symptoms of cervicothoracal osteochondrosis include:
- dysfunction of the muscles of the neck, skin, hands and face;
- headaches and dizziness;
- unsteady walking;
- increased fatigue, impaired vision and hearing.
The pain radiates to the arm, extending from the shoulder to the fingertips, causing numbness of the skin, even slight movement of the neck, can cause a feeling of electric current along the entire arm.
Myelopathy can cause:
- disorders of the lungs and heart;
- double vision;
- numbness of the tongue.
Treatment of exacerbation of the disease
The use of complex therapy in the treatment of exacerbation of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis allows a lasting positive result to be achieved. Includes:
- The method of orthopedic correction is to fix the neck with a Chance collar, which supports the head, significantly relieving the load on the cervical vertebrae and contributing to their alignment.
- The method is pharmacopuncture - anti - inflammatory drugs (preferably homeopathic) to relax spasmodic muscles and prevent exacerbation of radical compression.
- Chondroprotectors - to prevent cartilage damage.
- Medicines that help strengthen the cartilage strips on the cartilage discs.
- Acupuncture is used to quickly relieve pain, relieve muscle cramps, and restore spinal nerve function. This method is very effective and its use during exacerbation prevents the disease from progressing for many years.
- Hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches promotes scarring of damaged fibrous rings in the cartilage discs, eliminates edema of the nerve roots, and improves blood circulation in the cartilage discs of the spine.
- Drug therapy - biogenic stimulants, drugs that improve peripheral circulation, vitamins.
- Massage - to relax, restore and strengthen cramped muscles.
In the last stage of treatment, in addition to eliminating muscle cramps and inflammatory processes, they are connected - manual therapy, osteopathy, training therapy.
Timely treatment of any disease prevents exacerbations and the various complications they cause.



































